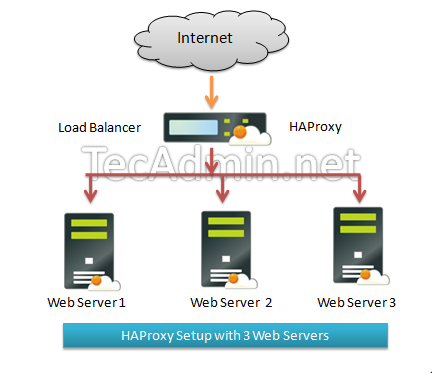
This article will help you to setup HAProxy load balancing environment on Ubuntu, Debian and LinuxMint. This will configure a Layer 4 Load Balancing (Transport Layer). Which will balance load and transfer requests to different-2 servers based on IP address and port numbers.
Network Details –
Below is our network server. There are 3 web servers running with Apache2 and listening on port 80 and one HAProxy server.Web Server Details: Server 1: web1.example.com 192.168.1.101 Server 2: web2.example.com 192.168.1.102 Server 3: web3.example.com 192.168.1.103HAProxy Server: HAProxy: haproxy 192.168.1.12
Step 1 – Install HAProxy
Now start the setup. SSH to your haproxy server as privileged user and install HAProxy using following commands.$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:vbernat/haproxy-1.5 $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install haproxy
Step 2 – Load Balancing Configuration with HAProxy
Now edit haproxy default configuration file /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg and start configuration.# vi /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
Default Settings:
You will find some default configuration like below. If you don’t have enough idea about this, you can keep as it is.global log /dev/log local0 log /dev/log local1 notice chroot /var/lib/haproxy stats socket /run/haproxy/admin.sock mode 660 level admin stats timeout 30s user haproxy group haproxy daemon # Default SSL material locations ca-base /etc/ssl/certs crt-base /etc/ssl/private # Default ciphers to use on SSL-enabled listening sockets. # For more information, see ciphers(1SSL). This list is from: # https://hynek.me/articles/hardening-your-web-servers-ssl-ciphers/ ssl-default-bind-ciphers ECDH+AESGCM:DH+AESGCM:ECDH+AES256::RSA+AES:RSA+3DES:!aNULL:!MD5:!DSS ssl-default-bind-options no-sslv3defaults log global mode http option httplog option dontlognull timeout connect 5000 timeout client 50000 timeout server 50000 errorfile 400 /etc/haproxy/errors/400.http errorfile 403 /etc/haproxy/errors/403.http errorfile 408 /etc/haproxy/errors/408.http errorfile 500 /etc/haproxy/errors/500.http errorfile 502 /etc/haproxy/errors/502.http errorfile 503 /etc/haproxy/errors/503.http errorfile 504 /etc/haproxy/errors/504.http
Adding HAProxy Listener:
Now tell HAProxy to where to listen for new connections. As per below configuration HAProxy will listed on port 80 of 192.168.1.12 ip address.frontend Local_Server bind 192.168.1.12:80 mode http default_backend My_Web_Servers
Add Backend Web Servers:
As per above configuration haproxy is now listening on port 80. Now define the backend web servers where HAProxy send the request.backend nodes mode http balance roundrobin option forwardfor http-request set-header X-Forwarded-Port %[dst_port] http-request add-header X-Forwarded-Proto https if { ssl_fc } option httpchk HEAD / HTTP/1.1rnHost:localhost server web1.example.com 192.168.1.101:80 server web2.example.com 192.168.1.102:80 server web3.example.com 192.168.1.103:80
Enable HAProxy Stats (Optional)
Now if you want you can enable Haproxy statistics by adding following configuration in HAProxy configuration file.listen stats *:1936 stats enable stats hide-version stats refresh 30s stats show-node stats auth username:password stats uri /stats
Step 3 – Final HAProxy Configuration File
The final configuration file may look like below .global log /dev/log local0 log /dev/log local1 notice chroot /var/lib/haproxy stats socket /run/haproxy/admin.sock mode 660 level admin stats timeout 30s user haproxy group haproxy daemon # Default SSL material locations ca-base /etc/ssl/certs crt-base /etc/ssl/private # Default ciphers to use on SSL-enabled listening sockets. # For more information, see ciphers(1SSL). This list is from: # https://hynek.me/articles/hardening-your-web-servers-ssl-ciphers/ ssl-default-bind-ciphers ECDH+AESGCM:DH+AESGCM:ECDH+AES256::RSA+AES:RSA+3DES:!aNULL:!MD5:!DSS ssl-default-bind-options no-sslv3defaults log global mode http option httplog option dontlognull timeout connect 5000 timeout client 50000 timeout server 50000 errorfile 400 /etc/haproxy/errors/400.http errorfile 403 /etc/haproxy/errors/403.http errorfile 408 /etc/haproxy/errors/408.http errorfile 500 /etc/haproxy/errors/500.http errorfile 502 /etc/haproxy/errors/502.http errorfile 503 /etc/haproxy/errors/503.http errorfile 504 /etc/haproxy/errors/504.httpfrontend Local_Server bind 192.168.1.12:80 mode http default_backend My_Web_Serversbackend My_Web_Servers mode http balance roundrobin option forwardfor http-request set-header X-Forwarded-Port %[dst_port] http-request add-header X-Forwarded-Proto https if { ssl_fc } option httpchk HEAD / HTTP/1.1rnHost:localhost server web1.example.com 192.168.1.101:80 server web2.example.com 192.168.1.102:80 server web3.example.com 192.168.1.103:80listen stats *:1936 stats enable stats hide-version stats refresh 30s stats show-node stats auth username:password stats uri /stats
Step 4 – Restart HAProxy
Now you have made all necessary changes in your HAProxy server. Now verify configuration file before restarting service using following command.$ haproxy -c -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfgIf above command returned output as configuration file is valid then restart HAProxy service
$ sudo service haproxy restart
Step 5 – Verify HAProxy Setting
At this stage we have full functional HAProxy setup. At each web server node I have a demo index.html page showing servers hostname, So we can easily differentiate between servers web pages.Now access port 80 on ip 192.168.0.12 (as configured above) in web browser and hit refresh. You will see that HAProxy is sending requests to backend server one by one (as per round robin algorithm).
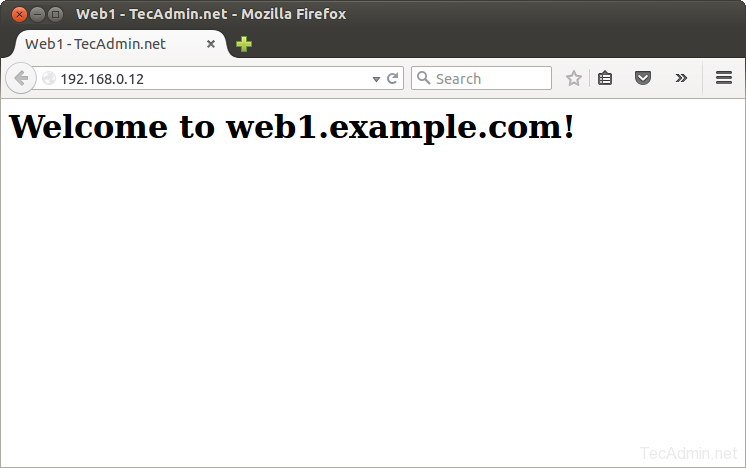
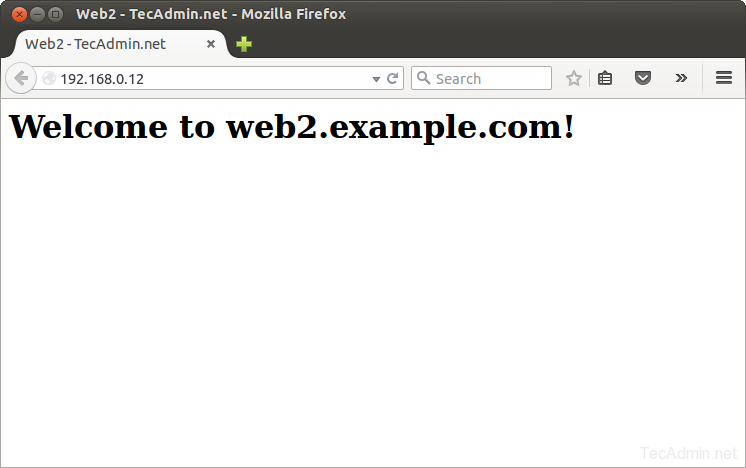
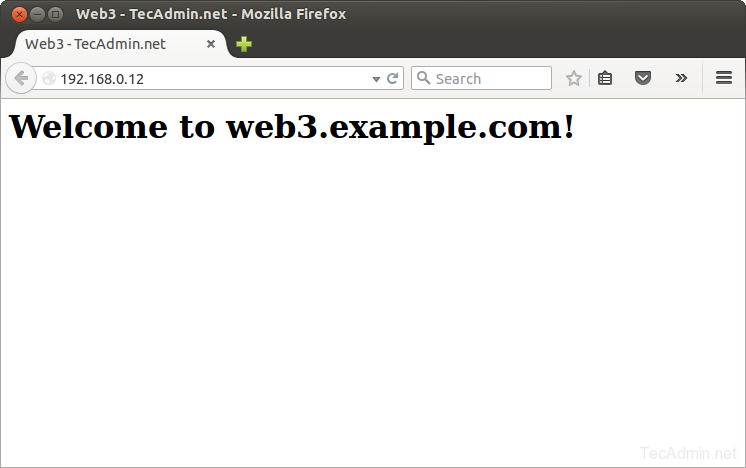
With each refresh you can that HAProxy is sending request one by one to backend server.
Reference: http://www.haproxy.org/download/1.5/doc/configuration.txt
Comments
Post a Comment